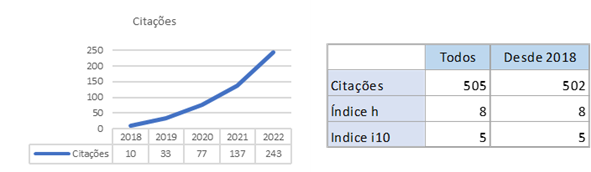
Maintenance of Pulmonary Rehabilitation’ effects in patients with COPD
development of a complex intervention
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.33194/rper.2025.41523Keywords:
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, Rehabilitation, Education, NursingAbstract
Introduction: Optimizing health condition and improving quality of life in patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease represents an area of focus within healthcare. Although pulmonary rehabilitation programs are part of the core of interventions designed for disease’ control and management, their effect is limited and short-lived over time if there is no strategy for maintenance and follow-up.
The present study aims to develop and identify a complex nursing intervention that, when integrated into a pulmonary rehabilitation program, can contribute to improving symptom management and promoting the maintenance of acquired healthy behaviors, as well as extending the benefits of the program in people with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD).
Methodology: The study design is based on the model of complex interventions and, the development of the intervention involved a set of strategies and methods necessary for better systematization and organization of concepts, including a systematic literature review, meetings with the rehabilitation nurses, analysis of documentation, and learning sessions for the health care team.
Conclusion: The final result consists of a complex intervention that implemented over the course of a 12-month program, including an initial pulmonary rehabilitation program (3 months), followed by a maintenance component supported by phone calls over 9 months, to reinforce the learned content and help engage individuals.
Downloads
References
1.Observatório Nacional das Doenças Respiratórias. Relatório. Lisboa: Fundação Portuguesa do Pulmão; 2024. Disponível em: https://www.fundacaoportuguesadopulmao.org/destaques/conteudos/ondr-2024/
2.Ebadi Z, Goërtz YMJ, Van Herck M, Janssen DJA, Spruit MA, Burtin C, et al. The prevalence and related factors of fatigue in patients with COPD: A systematic review. Eur Respir Rev. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1183/16000617.0298-2020
3.GOLD. Global Strategy for Prevention, Diagnosis and Management of COPD: Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease; 2025. Disponível em: https://goldcopd.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/GOLD-2025-Report-v1.0-15Nov2024_WMV.pdf
4.Merlo C, Bernardi E, Bellotti F, Pomidori L, Cogo A. Supervised exercise training improves endothelial function in COPD patients: A method to reduce cardiovascular risk? ERJ Open Res. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1183/23120541.00304-2019
5.Gordon CS, Waller JW, Cook RM, Cavalera SL, Lim WT, Osadnik CR. Effect of pulmonary rehabilitation on symptoms of anxiety and depression in COPD: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Chest. 2019 Jul;156(1):80-91. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2019.04.009
6.Pereira MAS, Moreira AFB, Machado PAP, Padilha JMSC. Impacte da reabilitação respiratória, prescrita por enfermeiros, na capacidade para o autocuidado, na pessoa com DPOC. Rev Port Enferm Reabil. 2020;3(2):80-85. http://dx.doi.org/10.33194/rper.2020.v3.n2.12.5823
7.Troosters T, Janssens W, Demeyer H, Rabinovich RA. Pulmonary rehabilitation and physical interventions. Eur Respir Rev. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1183/16000617.0222-2022
8. Agusti A, Ambrosino N, Blackstock F, Bourbeau J, Casaburi R, Celli B, et al. COPD: Providing the right treatment for the right patient at the right time. Respir Med. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rmed.2022.107041
9.Padilha JM, Sousa PAF, Pereira FM. Analysis of use of technological support and information content by patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Acta Paul Enferm. 2012;25(Spe1):60-66. http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/s0103-21002012000800010
10.Spruit MA, Singh SJ, Garvey C, ZuWallack R, Nici L, Rochester C, et al. ATS/ERS Task Force on Pulmonary Rehabilitation. An official American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society statement: key concepts and advances in pulmonary rehabilitation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013 Oct 15;188(8):e13-64. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201309-1634ST. Erratum in: Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2014 Jun 15;189(12):1570. PMID: 24127811.
11.Spruit MA, Singh SJ. Maintenance programs after pulmonary rehabilitation: how may we advance this field? Chest. 2013 Oct;144(4):1091-1093. doi: 10.1378/chest.13-0775. PMID: 24081336.
12.Armstrong M, Hume E, McNeillie L, Chambers F, Wakenshaw L, Burns G, et al. Behavioural modification interventions alongside pulmonary rehabilitation improve COPD patients’ experiences of physical activity. Respir Med. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rmed.2021.106353
13.Silva L, Maricoto T, Costa P, Berger-Estilita J, Padilha JM. A meta-analysis on the structure of pulmonary rehabilitation maintenance programmes on COPD patients’ functional capacity. NPJ Prim Care Respir Med. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41533-022-00302-x
14.Coll F, Cavalheri V, Gucciardi DF, Wulff S, Hill K. In people with COPD, there is limited evidence that exercise training reduces sedentary time, and behavior change techniques are poorly reported: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Phys Ther. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1093/ptj/pzab097
15.Skivington K, Matthews L, Simpson SA, Craig P, Baird J, Blazeby JM, et al. A new framework for developing and evaluating complex interventions: update of Medical Research Council guidance. BMJ. 2021 Sep 30;374:n2061. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n2061. PMID: 34593508; PMCID: PMC8482308.
16.European Academy of Nursing Science. European Academy of Nursing Science. Disponível em: https://www.eansnursing.eu/. Acedido em 16 de abril de 2025.
17.O'Cathain A, Croot L, Duncan E, et al. Guidance on how to develop complex interventions to improve health and healthcare. BMJ Open. 2019;9:e029954. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2019-029954
18.Padilha JM, Sousa AP, Pereira FM. Participatory action research: A strategy for improving self-care management in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients. Action Res. 2016;14(3):240-256. https://doi.org/10.1177/1476750315606196
19.Pinto D, Spencer L, Pereira S, Machado P, Sousa P, Padilha M. Maintaining effects of pulmonary rehabilitation at home in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A systematic literature review. Home Health Care Manag Pract. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1177/1084822321990376
20.Teixeira PJ, Marques MM, Silva MN, Brunet J, Duda JL, Haerens L, et al. A classification of motivation and behavior change techniques used in self-determination theory-based interventions in health contexts. Motiv Sci. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1037/mot0000172
21.Alghamdi SM. Content, mechanism, and outcome of effective telehealth solutions for management of chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases: A narrative review. Healthcare (Basel). 2023 Dec 14;11(24):3164. doi: 10.3390/healthcare11243164. PMID: 38132054; PMCID: PMC10742533.
22.Malaguti C, Dal Corso S, Janjua S, Holland AE. Supervised maintenance programmes following pulmonary rehabilitation compared to usual care for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD013569.pub2
23.Candemir I, Ergun P, Kaymaz D, Demir N, McCurdy SA. Comparison of unsupervised home-based pulmonary rehabilitation versus supervised hospital outpatient pulmonary rehabilitation in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Expert Rev Respir Med. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1080/17476348.2019.1675516
24.Wootton S, McKeough Z, Ng CLW, Jenkins S, Hill K, Eastwood PR, et al. Effect on health-related quality of life of ongoing feedback during a 12-month maintenance walking programme in patients with COPD: A randomized controlled trial. Respirology. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1111/resp.13128
25.Spencer LM, McKeough ZJ. Maintaining the benefits following pulmonary rehabilitation: Achievable or not? Respirology. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1111/resp.13518
26.Burge AT, Holland AE, McDonald CF, Abramson MJ, Hill CJ, Lee AL, et al. Home-based pulmonary rehabilitation for COPD using minimal resources: An economic analysis. Respirology. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1111/resp.13667
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Portuguese Rehabilitation Nursing Journal

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.